Whale evolution
One strange creature that we find is the whale. Surprisingly whales are genetically far more similar to other mammals than to fish even though they look like fish. Whales may look like fish on the outside, but they are far different on the inside, and are actually mammals.
Whales have hair, a trait found in mammals not fish. Whales give birth to live young and don't lay eggs like fish. They feed their young with breast-milk which is a mammal trait not seen in fish. Whales have smooth skin not fish scales. Whales move their tails up and down when swimming, a mammal trait. Fish move their tails side to side. Whales have pelvises just like mammals, and have a hand structure in their front fins unlike fish.
The below links show the fish and whale skeletons compared.

The most important feature of all is that whales have lungs instead of gills. This would be comparable to making a monkey with gills instead lungs. This monkey would live and eat up in the trees, but from time to time they will have to rush back in the water to breathe. Dolphins are also mammals that look like fish.
Whales also have a four-chambered stomach which is a super-stomach meant to grind up grass and leaves that most other animals can't really use. However whales don't eat grass or leaves but they do eat tiny sea creatures called krill, and zooplankton. They also eat tiny single-celled algae, fish, squid, shrimp, marine mammals and birds. Of course different whales have different specialized diets. Whales do not need four-chambered cattle stomachs to eat sea creatures, so a four-chambered stomach is very unnecessary. Having a four-chambered stomach is like cutting paper with a chain saw.
This makes sense from an evolutionary view because whales are most related to cattle which eat grass and leaves, and so inherited their stomachs. The closest land-mammals relative of the whale, the hippo lived mostly in the water, exhibiting a life-style maybe very near that of the ancestors of whales, and eats grass.
The reason for this is that millions of years ago, some land animals that lived in shallow water began adapting themselves more and more for water with fins and the like, until they could not live in the water any-more. This is why whales look like mammals dressed up like fish. The hippo a close relative of whales hints at the possible lifestyle of these ancestors.
In fact we find transitional fossils of land animals evolving into whales.
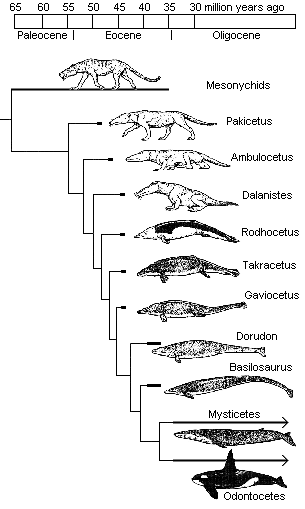
The above image shows the evolution of whales with more whale-like creatures in higher geological strata. This evolutionary series starts out in 50 million year old strata and becomes more and more whale-like as we approach 35 million year old strata. We find these fossils in Pakistan.

The above link shows the skeletons of the transitionals.
Notice how the front arms are becoming reduced as we go into higher strata. Also notice how the back legs disappear and the pelvis becomes small and distant from the spine. Indeed Dorudon has a transitional pelvis between that of a normal mammal and that of a whale. Notice also how the transitionals increase in size over time.
Richard Dawkins on whale evolutionThis two minute video shows how the nose of the mammal ancestors of the whale starts moving up the forehead to become the blow-hole of the whale as we look at more and more whale-like fossils.
Looking at the whale pelvis, we see that it is vestigial. It is tiny and just sitting separated from the spine in the whale. Lets take a closer look on this pelvis.

As you see, it still has the femur which is a leg bone. This is an astounding piece of evidence for evolution.
It is doubtful if this pelvis has any function at all, although it might have some minor function. It is vestigial because it has lost its former function (holding the legs solidly).
29+ evidences for evolution and dolphin embryosIndeed in the above link, we find that some dolphin species still develop leg bugs in embryonic development. What evolution did was keep the leg buds from developing further into legs; in the dolphins. The embryonic evidence is screaming out who the ancestors of whales are.
Evolution and atavisms Edward t Babinski on whales and atavismsThe most astounding thing of all is that sometimes unlucky whales and dolphins will develop atavistic legs on their vestigial pelvises! Atavisms are traits formed from ancestral genes that were turned off, but through some mutation is turned back on in a descendent. Often these genes will allow something which started in embryonic development (leg buds) to continue to develop and not stop.
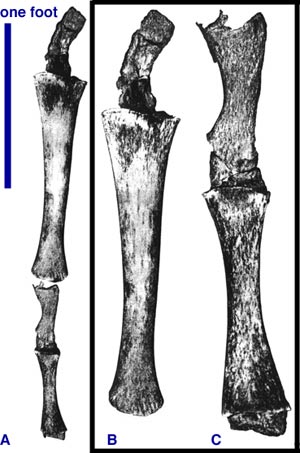
Everything about the whale screams of its origins. The fossil record shows the ancestry of the whale. Whales are strong evidence for the theory of evolution.
Edited by dan4reason, : No reason given.
Edited by Admin, : Reduce image width.

 ™ Version 4.2
™ Version 4.2